In this chapter, we will share five useful mathematical functions in Java for performing mathematical operations. However, before that, we will first explain a topic that bridges the past and the future – operators. Whether it is used in mathematical operations or the logical operators that will be introduced later for conditional judgment, operators are used to tell the compiler what to execute using symbols. This is something that is well worth knowing!!!
Arithmetic Operators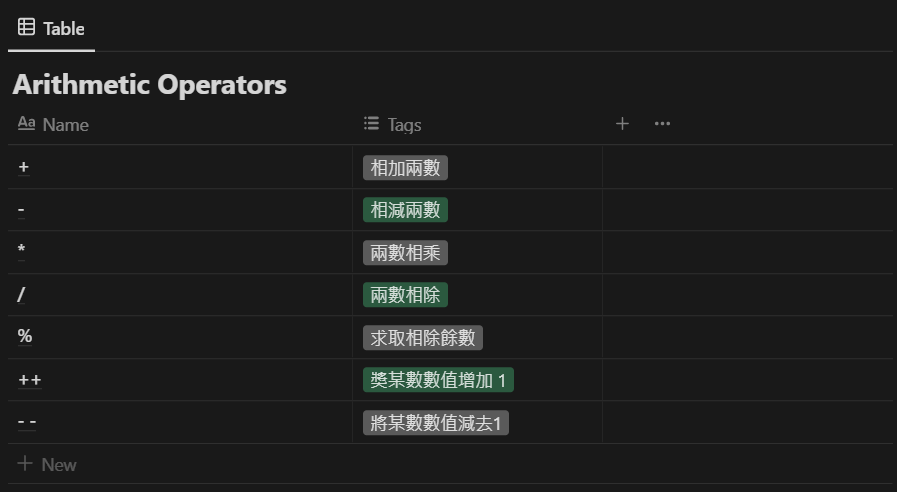
Assignment operators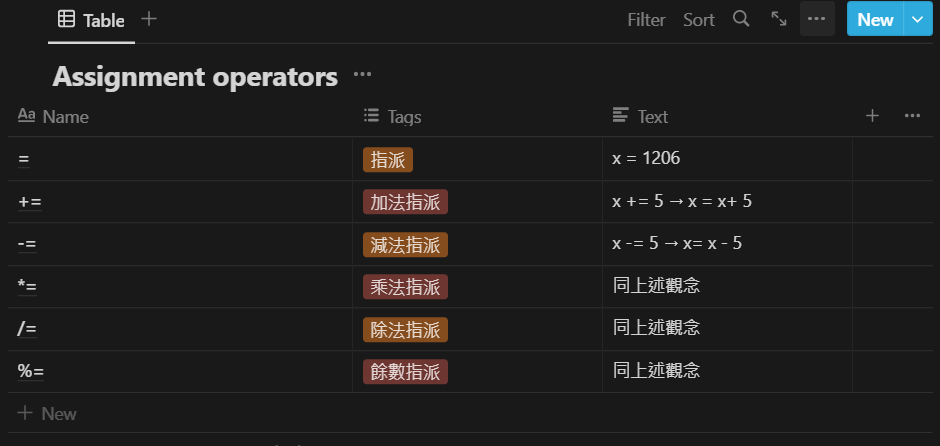
Comparison operators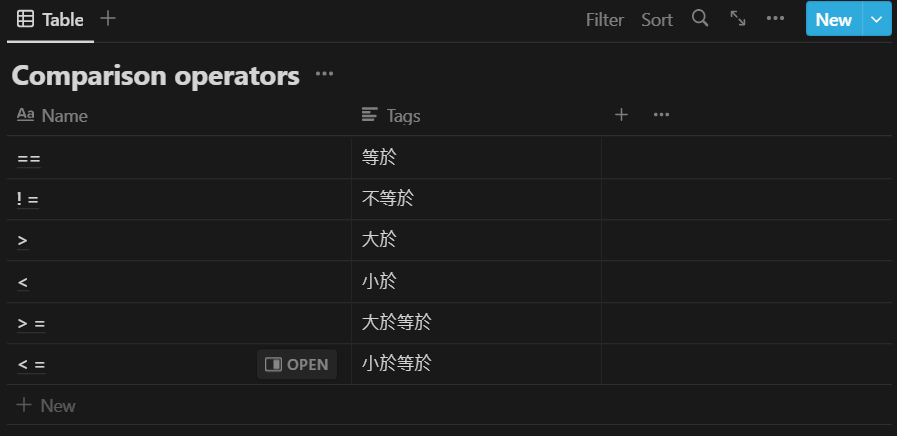
Logical operators
Bitwise operators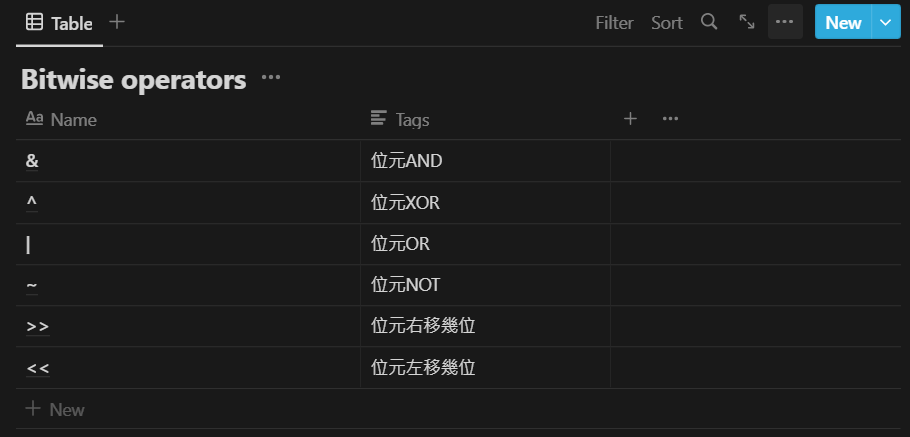
The following describes the application of mathematical functions and provides program examples to complement the content of the above operators:
public class Main(){
public static void main(String[] agrs){
int x = 10, y = 11;
int max,min;
max = Math.max(x,y); //max = 11
min = Math.min(x,y); //min = 10
max -= 1; //max = 10
min++; //min = 11
if(max == min) System.out.println("Hello!");
else if(max > min) System.out.println("Hola!!");
else System.out.println("你好!!!") //Outputs : 你好!!!
}
}
public class Main(){
public static void main(String[] args){
int root;
root = Math.sqrt(100); //Outputs : 10
root /= -10;
Syestem.out.println(Math.abs(root)); //Outputs : 1
}
}
public class Main(){
public static void main(String[] args){
int random;
random = (int)(Math.random() * 101 );
System.out.println(random); //Outputs : random number between 0~100
}
}
Program analysis: We can see that there is a special usage in line 4 (int) This is to ensure that the random variable generated later is a decimal point, and to make it without a decimal point, we use the method of “forced conversion”. Forced conversion involves type conversion between variables, and the following provides a casting sequence between variables.
From small to large, a forced conversion is required for small to large, while no conversion is required for large to small.
byte-> short-> char-> int-> long-> float-> double
![]()
